The purpose of accounting
/What is the Purpose of Accounting?
The purpose of accounting is to accumulate and report on financial information about the performance, financial position, and cash flows of a business. This information is then used to reach decisions about how to manage the business, or invest in it, or lend money to it. This information is accumulated in accounting records with accounting transactions, which are recorded either through such standardized business transactions as customer invoicing or supplier invoices, or through more specialized transactions, known as journal entries.
Types of Financial Statements
Once this financial information has been stored in the accounting records, it is usually compiled into financial statements, which include the following documents:
Income statement. This report shows the net sales of a business for a reporting period, from which expenses are deducted to arrive at a profit or loss.
Balance sheet. This report shows the ending balances of a firm’s assets, liabilities, and equity as of the end of a reporting period.
Statement of cash flows. This report shows the inflows and outflows of cash experienced by an organization during a reporting period, within various categories.
Statement of retained earnings. This report shows changes in the various classifications of retained earnings during a reporting period, such as increases due to earnings, and deductions due to dividend payouts.
Financial statement footnotes. These disclosures are mandated by accounting standards, and can span a broad array of accounting issues relating to the financial statements.
Related AccountingTools Courses
Accounting Frameworks
Financial statements are assembled under certain sets of rules, known as accounting frameworks, of which the best known are Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). The results shown in financial statements can vary somewhat, depending on the framework used. The framework that a business uses depends upon which one the recipient of the financial statements wants. Thus, a European investor might want to see financial statements based on IFRS, while an American investor might want to see statements that comply with GAAP.
Managerial Reports
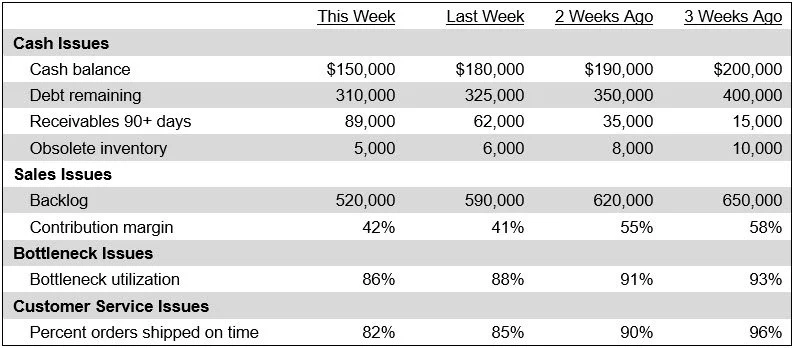
The accountant may generate additional reports for special purposes, such as determining the profit on sale of a product, or the revenues generated from a particular sales region. These are usually considered to be managerial reports, rather than the financial reports issued to outsiders. An example of a managerial report appears in the following exhibit, which displays a flash report that itemizes the key operational and accounting issues of a business.
Thus, the purpose of accounting centers on the collection and subsequent reporting of financial information.