Comprehensive income definition
/What is Comprehensive Income?
Comprehensive income is the change in the equity of a business during a reporting period, not including the purchase or sale of stock or the distribution of dividends. This change is comprised of net income or net loss, and other comprehensive income. The other comprehensive income classification includes the following items:
Available-for-sale securities fair value changes that were previously written down as impaired
Available-for-sale securities unrealized gains and unrealized losses
Cash flow hedge derivative instrument gains and losses
Debt security unrealized gains and losses arising from a transfer from the available-for-sale category to the held to maturity category
Foreign currency gains and losses on intra-entity currency transactions where settlement is not planned or anticipated in the foreseeable future
Foreign currency transaction gains and losses that are hedges of an investment in a foreign entity
Foreign currency translation adjustments
Pension or post-retirement benefit plan gains or losses
Pension or post-retirement benefit plan prior service costs or credits
Pension or post-retirement benefit plan transition assets or obligations that are not recognized as a component of the net periodic benefit or cost
The comprehensive income classification presents a more complete view of a firm’s income than can be found in a traditional income statement. It emphasizes changes in the equity of the reporting business, which represents a broader view of income than just net income.
Related AccountingTools Course
Presentation of Comprehensive Income
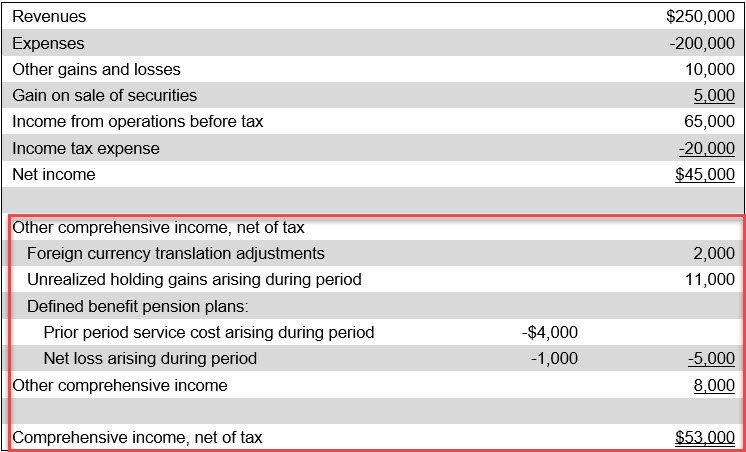
A sample presentation of comprehensive income appears in the following income statement exhibit, where the comprehensive income line items are reported below the revenue, expense, and net income information for a business.
FAQs
How Does Comprehensive Income Differ From Net Income?
Net income includes revenues, expenses, gains, and losses that result from a company’s normal operations during a period. Comprehensive income goes further by including both net income and other comprehensive income, which captures items that bypass the income statement, such as unrealized investment gains, foreign currency translation adjustments, and pension adjustments. This makes comprehensive income a broader measure of total changes in equity compared to net income alone.