Aging schedule definition
/What is an Aging Schedule?
An aging schedule is a report that itemizes payables and receivables into different categories based on their creation dates. The report is used to show which items are overdue, either for payment or receipt. The schedule is typically divided into 30-day categories, so that current items are stated in the 0-30 days category, moderately overdue items are in the 31-60 days category, and very overdue items are stated in later categories. The report is a standard feature in all accounting software packages, which may also allow a user to set up different day ranges than the 30-day classifications just noted. The schedule has the uses noted below.
Payables Aging Schedule
The payables aging is used for deciding when to pay accounts payable. This is a somewhat less useful schedule, because some suppliers demand rapid invoice payment, while others may allow quite delayed payments. The result is a scattering of payment line items across the date buckets in the report. In this case, a better approach to examining the payment timing of supplier invoices is to review them on a supplier-by-supplier basis.
Receivables Aging Schedule
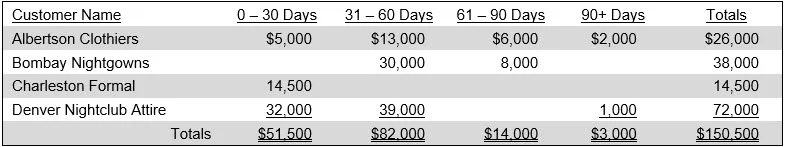
The receivables aging is used for deciding when to initiate collection activities on overdue accounts receivable, when to write off a receivable as a bad debt, and when to refer a receivable to a collection agency. The aging may also be used to estimate the total amount of bad debt, which is useful for calculating the most appropriate amount to have in the allowance for doubtful accounts. Yet another use is that a company's credit department can examine it to decide whether a customer should be granted more or less credit. A sample receivables aging schedule appears in the following exhibit.
Both the payable and receivable aging schedules can be used to compile a cash forecast for a business.
Related AccountingTools Courses
Credit and Collection Guidebook