Throughput analysis definition
/What is Throughput Analysis?
The primary concept underpinning throughput analysis is that you should look at investment decisions in terms of their impact on the entire system, rather than on the specific area in which an investment is contemplated. The system view is based on the fact that most production costs do not vary at the level of the individual unit produced. When a unit is manufactured, only the associated cost of materials is incurred. All other costs are associated with the production process, and so will be incurred even in the absence of any unit-level production.
For example, in order to operate a production line at all, there must be a conveyor belt, production equipment, and a minimum number of employees to staff the line. Irrespective of the presence of any production activity, these costs must still be incurred. Consequently, the focus of attention should be on the process that produces goods, rather than on the goods themselves.
Related AccountingTools Course
The Throughput Analysis Approach
The system approach advocated by throughput analysis uses a whole new set of terms, rather than the cost of goods sold and gross margin concepts that are most commonly applied to units produced. The following concepts are of particular importance:
Throughput. This is sales minus totally variable expenses, which usually translates into sales minus the cost of direct materials, and perhaps commissions. Because so few costs are truly variable, throughput as a percentage of sales should be quite high.
Operating expenses. This is all expenses, not including the totally variable expenses used in the calculation of throughput. In essence, these are all of the costs required to maintain the system of production. Operating expenses may have some variable cost characteristics, but are generally fixed costs.
Investment. This is the amount of cash invested in order to increase the capacity of the production system to produce more units.
These concepts are included in the following three formulas, which are used to solve a number of financial analysis scenarios:
Revenue – totally variable expenses = throughput
Throughput – operating expenses = net profit
Net profit / investment = return on investment
Questions to Answer in Throughput Analysis
When altering the system of production, one or more of the preceding formulas can be used to decide whether the contemplated alteration will improve the system. There must be a positive answer to one of the following questions, or else no action should be taken:
Is there an incremental increase in throughput?
Is there an incremental reduction in operating expenses?
Is there an incremental increase in the return on investment?
The best system improvements are those that increase the amount of throughput generated, since there is no theoretical upper boundary on the amount of throughput. Conversely, an action taken to reduce operating expenses is less important, since expenses can only be reduced to zero. Also, be wary of any decisions to reduce operating expenses that pose the risk of also reducing the maximum effective capacity of the production system, since this may impinge upon throughput. The latter type of suggest is routinely brought up by accountants, who focus less on capacity and more on expense reduction.
Example of Throughput Analysis
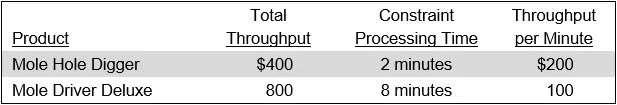
Mole Industries manufactures trench digging equipment. It has two products with different amounts of throughput and processing times at the constrained resource. The key information about these products is:
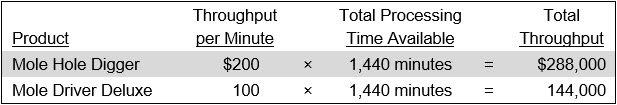
Of the two products, the Mole Driver Deluxe creates the most overall throughput, but the Mole Hole Digger creates more throughput per minute of constraint processing time. To determine which one is more valuable to Mole Industries, consider what would happen if the company had an unlimited order quantity of each product, and could run the constrained resource nonstop, all day (which equates to 1,440 minutes). The operating results would be:
Clearly, the Mole Hole Digger, with its higher throughput per minute, is much more valuable to Mole Industries than its Mole Driver Deluxe product. Consequently, the company should push sales of the Mole Hole Digger product whenever possible.
Advantages of Throughput Analysis
There are many advantages to throughput analysis, which include the following:
Identifies bottlenecks. Throughput analysis helps to pinpoint specific stages in a process where delays or inefficiencies occur.
Enhances resource utilization. Throughput analysis assists in optimizing the use of resources, such as labor, equipment, and materials, to maximize output.
Maximizes profitability. Throughput analysis focuses on increasing throughput, so that you can generate more revenue from the same set of resources.
Supports decision-making. Throughput analysis provides data-driven insights into the performance of a system or process.
Encourages system-wide thinking. Throughput analysis promotes a holistic view of a system, ensuring that all components work cohesively. It also avoids localized optimizations that may not benefit the overall system.
Facilitates cost savings. Throughput analysis reduces the cost per unit by increasing throughput without significant increases in fixed costs.
Drives competitive advantage. Throughput analysis increases the profits of a business, which enhances its competitiveness.
Throughput analysis is a powerful tool for improving system performance, optimizing resource utilization, and increasing profitability. Its emphasis on bottlenecks, efficiency, and value delivery makes it an essential practice for businesses aiming to enhance their operational capabilities and remain competitive.