Financial statements definition
/What are Financial Statements?
Financial statements are a collection of summary-level reports about an organization's financial results, financial position, and cash flows. They include the income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows.
Advantages of Financial Statements
Financial statements are useful for the following reasons:
To determine the ability of a business to generate cash, and the sources and uses of that cash.
To determine whether a business has the capability to pay back its debts.
To track financial results on a trend line to spot any looming profitability issues.
To derive financial ratios from the statements that can indicate the condition of the business.
To investigate the details of certain business transactions, as outlined in the disclosures that accompany the statements.
To use as the basis for an annual report, which is distributed to a company’s investors and the investment community.
Related AccountingTools Courses
Disadvantages of Financial Statements
There are few downsides to issuing financial statements, which are as follows:
Reporting fraud. A possible concern is that financial statements can be fraudulently manipulated, leading investors to believe that the issuing entity has produced better results than was really the case. Such manipulation can also lead a lender to issue debt to a business that cannot realistically repay it.
Inaccurate basis for forecasts. Another concern is that financial statements are entirely historical in nature, and so can be misleading when used to project the future results of a business. For example, a business that relies on government contracts might report robust results for its most recent period, and yet have no additional sales on tap, since it just completed all of the contracts that it had been awarded.
The Balance Sheet
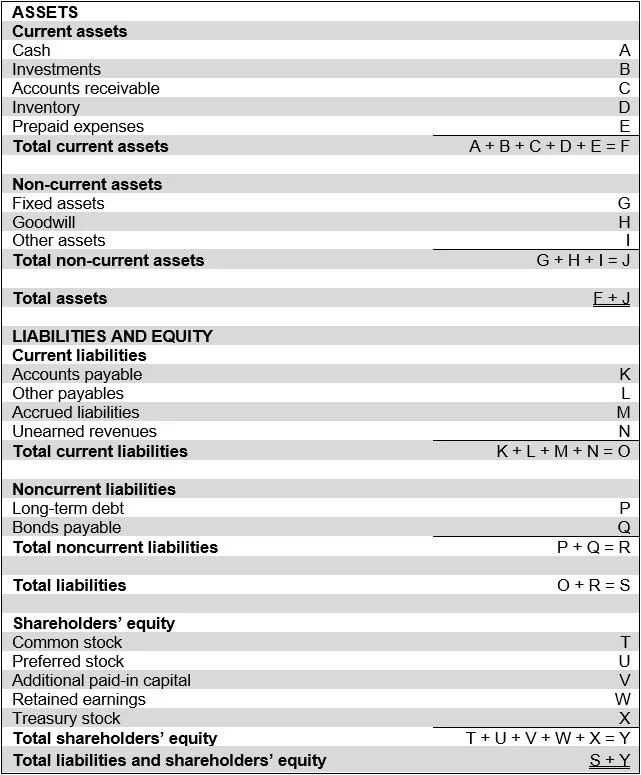
One of the financial statements is the balance sheet. It shows an entity's assets, liabilities, and stockholders' equity as of the report date. In this report, the total of all assets must match the combined total of all liabilities and equity. The asset information on the balance sheet is subdivided into current and long-term assets. Similarly, the liability information is subdivided into current and long-term liabilities. This stratification is useful for determining the liquidity of a business. Ideally, the total of all current assets should exceed the total of all current liabilities, which implies that a business has sufficient assets to pay off its current obligations. The balance sheet is also used to compare debt levels to the amount of equity invested in the business, to see if its leverage level is appropriate.
A balance sheet that shows how the information in each line item rolls up into the report totals appears in the next exhibit.
The Income Statement
Another financial statement is the income statement. It shows the results of an entity's operations and financial activities for the reporting period. It usually contains the results for either the past month or the past year, and may include several periods for comparison purposes. Its general structure is to begin with all revenues generated, from which the cost of goods sold is subtracted, and then all selling, general, and administrative expenses. The result is either a profit or loss, which is net of income taxes. This report is used to discern the ability of a business to generate a profit.
An income statement that shows how the information in each line item rolls up into the report totals appears in the next exhibit.
The Statement of Cash Flows
The final financial statement is the statement of cash flows. It shows changes in an entity's cash flows during the reporting period. These cash flows are divided into cash flows from operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. The bulk of all cash flows are generally listed in the operating activities section, which state the cash inflows and outflows related to the basic operations of the business, such as from changes in receivables, inventory, and payables balances. The investing activities section contains cash flows from the purchase or sale of investment instruments, assets, or other businesses. The financing activities section contains cash flows related to the acquisition or paydown of debt, dividend issuances, stock sales, and so forth. The presented information is useful for determining the sources and uses of cash, and also indicates a firm’s financing situation.
A statement of cash flows that shows how the information in each line item rolls up into the report totals appears in the next exhibit.
Supplementary Notes
When financial statements are issued to outside parties, then also include supplementary notes. These notes include explanations of various activities, additional detail on some accounts, and other items as mandated by the applicable accounting framework, such as GAAP or IFRS. The level and types of detail provided will depend on the nature of the issuing entity’s business and the types of transactions in which it engaged. A reporting entity only includes the minimum mandated amount in the supplementary notes (which can still be quite extensive), because it can be quite time-consuming to produce the disclosures.
Presentation of the Financial Statements
If a business plans to issue financial statements to outside users (such as investors or lenders), the financial statements should be formatted in accordance with one of the major accounting frameworks. These frameworks allow for some leeway in how financial statements can be structured, so statements issued by different firms even in the same industry are likely to have somewhat different appearances. Financial statements that are being issued to outside parties may be audited to verify their accuracy and fairness of presentation.
If financial statements are issued strictly for internal use, there are no guidelines, other than common usage, for how the statements are to be presented. If so, the controller generally uses a format that approximates the layout used for external reporting, though it may contain some additional detail that would be considered excessive by outsiders. The additional level of detail is used by managers to monitor the business.
At the most minimal level, a business is expected to issue an income statement and balance sheet to document its monthly results and ending financial condition. The full set of financial statements is expected when a business is reporting the results for a full fiscal year, or when a publicly-held business is reporting the results of its fiscal quarters.
Related Articles
How the Balance Sheet and Income Statement are Connected
Limitations of Financial Statements
The Purpose of Financial Statements